50 NUANCES D’IA
L’Encyclopedia Britannica définit l’Intelligence artificielle (IA) de la manière suivante : « cest la capacité d’un ordinateur ou d’un robot contrôlé par ordinateur à effectuer des tâches communément associées à des êtres intelligents. »
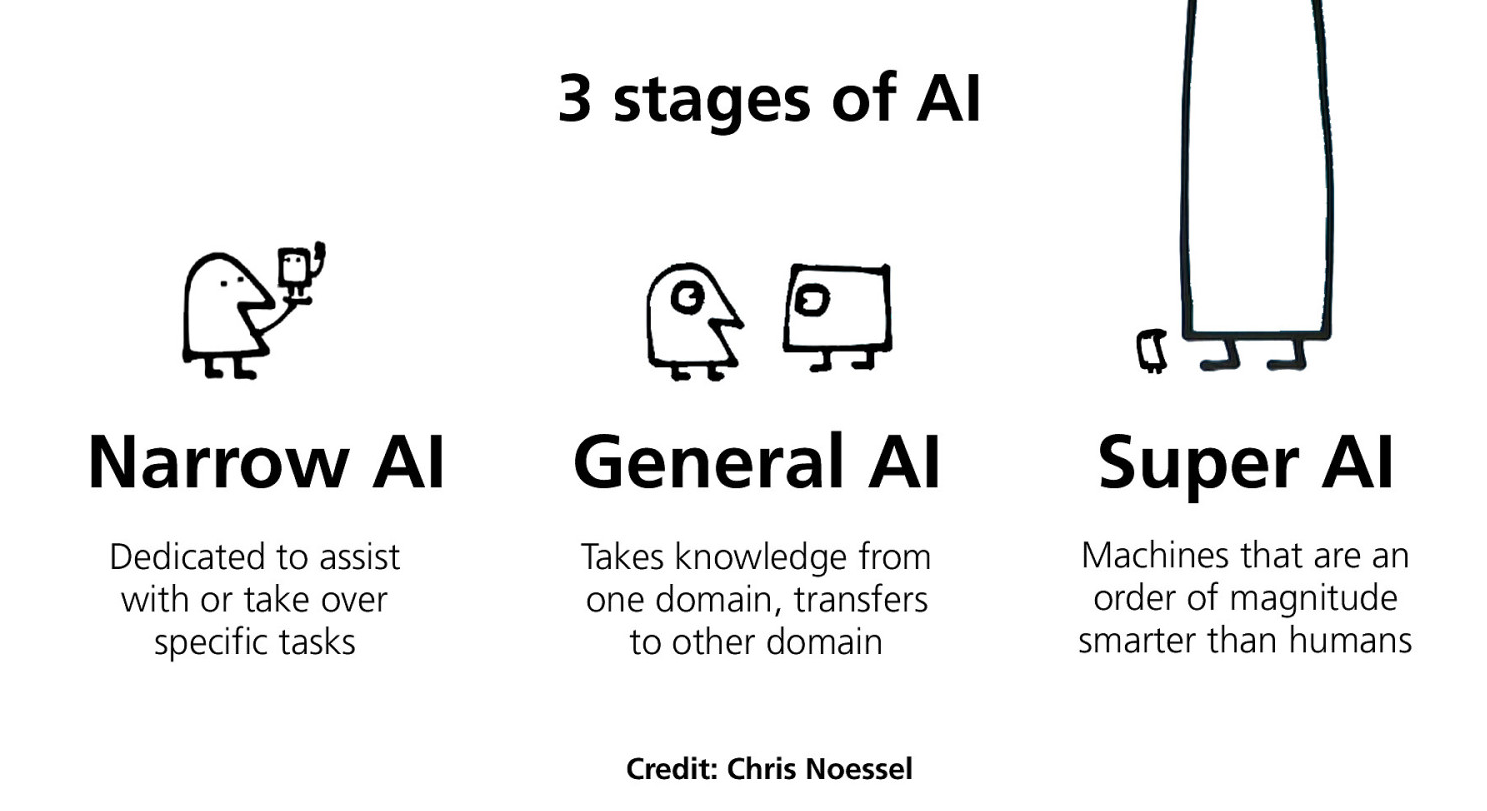
Il est important de noter que l’exécution de ces tâches ne nous dit pas à quel point l’ordinateur est intelligent. Cela n’implique pas nécessairement que l’ordinateur raisonne ou sait ce qu’il fait. C’est pourquoi nous distinguons communément l’IA en 3 sous-catégories (3 grandes nuances) :
- Narrow AI (IA restreinte) : accomplit des tâches spécifiques. Toutes les intelligences artificielles aujourd’hui sont restreintes
- General AI (IA généraliste) : est aussi performante qu’un humain dans les tâches de perception et est capable de raisonner
- Super AI : une IA aussi performante que tous les humains réunis
En quoi consiste la plupart des ia AUJOURD’HUI ?
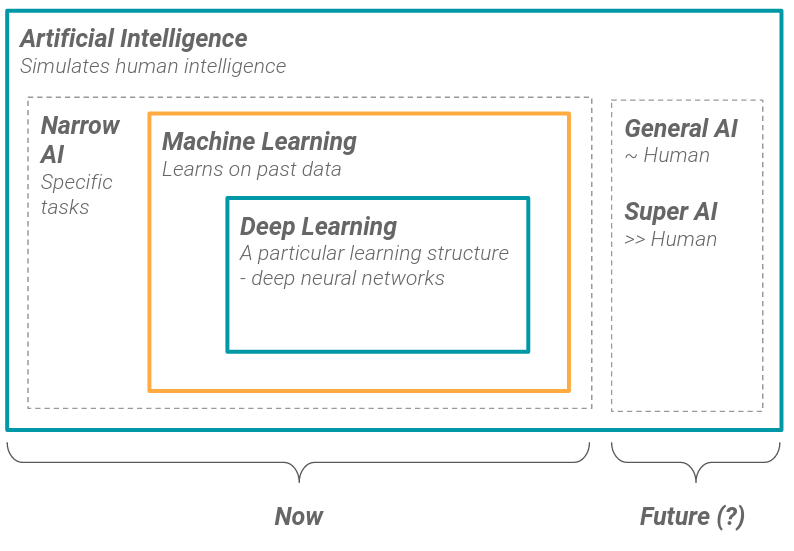
Elles consistent en la combinaison de deux choses : des données historiques en abondance et des algorithmes d’apprentissage automatique (Machine Learning).
L’apprentissage automatique, ou machine learning, est le processus par lequel un ordinateur est capable d’exécuter une tâche spécifique sans utiliser d’instructions explicites. Il atteint ce résultat en s’appuyant sur des modèles statistiques entraînés sur des données historiques.
Par exemple, un modèle d’apprentissage automatique ayant pour but de détecter automatiquement une espèce animale aura appris à partir de millions de photos d’animaux que les oreilles des chats sont pointues. Le modèle apprend cette information en prenant en entrée les pixels de l’image et en trouvant que le motif de pixels correspondant à l’oreille du chat est un bon moyen de distinguer les chats des oiseaux, des chiens et des autres espèces. Un autre ensemble de caractéristiques sera pris en compte par le modèle pour distinguer les chats des pandas rouges par exemple.
Il existe de nombreux algorithmes qui sont capables de détecter des motifs statistiques, ils peuvent être divisés en deux familles :
- Shallow learning (qu’on peut traduit comme l’apprentissage superficiel): par exemple les arbres de décision, les régressions linéaires
- Deep learning (apprentissage profond) : réseaux de neurones profonds avec de nombreuses couches cachées
Pour une plongée semi-technique dans l’apprentissage superficiel et l’apprentissage profond, vous pouvez lire ces deux posts de blog dédiés :
- 8 Algorithmes de Machine Learning expliqués en Language Humain
- 3 Algorithmes de Deep Learning expliqués en Langage Humain
CE qui l’ia n’est pas ?
Pour mettre les choses au clair, voici quelques éléments que l’IA n’est pas :
- Un cerveau humain par procuration. Les réseaux neuronaux sont beaucoup plus simples que le cerveau humain
- Un robot à aspect humain capable de raisonner
- Un ordinateur « je-sais-tout » capable de répondre à n’importe quelle question
- Un programme capable de prédire l’avenir avec une précision de 100%.
CONCLUSION
Pour résumer, les IA d’aujourd’hui accomplissent des tâches spécifiques, elles sont appelées IA restreintes. Cela peut déjà s’avérer extrêmement utile pour un large éventail d’industries et d’entreprises.
Les IA restreintes sont principalement basées sur l’apprentissage en profondeur, qui est un sous-domaine de l’apprentissage machine.
Les IA peuvent être combinées ensemble pour créer des systèmes complexes tels que des robots de type humain. Un tel robot peut être équipé des modèles suivants :
- Un modèle de marche (apprentissage par renforcement)
- Un modèle de détection d’objets et de personnes (apprentissage profond)
- Un modèle de reconnaissance des visages (apprentissage profond)
- Un modèle de lecture (apprentissage profond)
- Un modèle de jeu (Apprentissage du renforcement)
Au lieu d’une IA généraliste, c’est une combinaison d’IA restreintes qui fait les capacités des robots.
Les données et les ressources de calcul disponibles sont les facteurs clés de l’expansion des applications de l’IA dans le monde entier. Il y a deux défis majeurs pour l’IA aujourd’hui :
- Le défi à court terme est de démocratiser l’IA et de la déployer à grande échelle afin d’aider les entreprises et les organisations à tirer profit de cette incroyable technologie
- Le défi à long terme est de développer une IA généraliste capable de raisonner en combinant la recherche mathématique dans les domaines de l’apprentissage profond, de la théorie des graphes et de l’IA symbolique.