50 shades of AI
The Encyclopedia Britannica states, “artificial intelligence (AI), the ability of a digital computer or computer-controlled robot to perform tasks commonly associated with intelligent beings.”
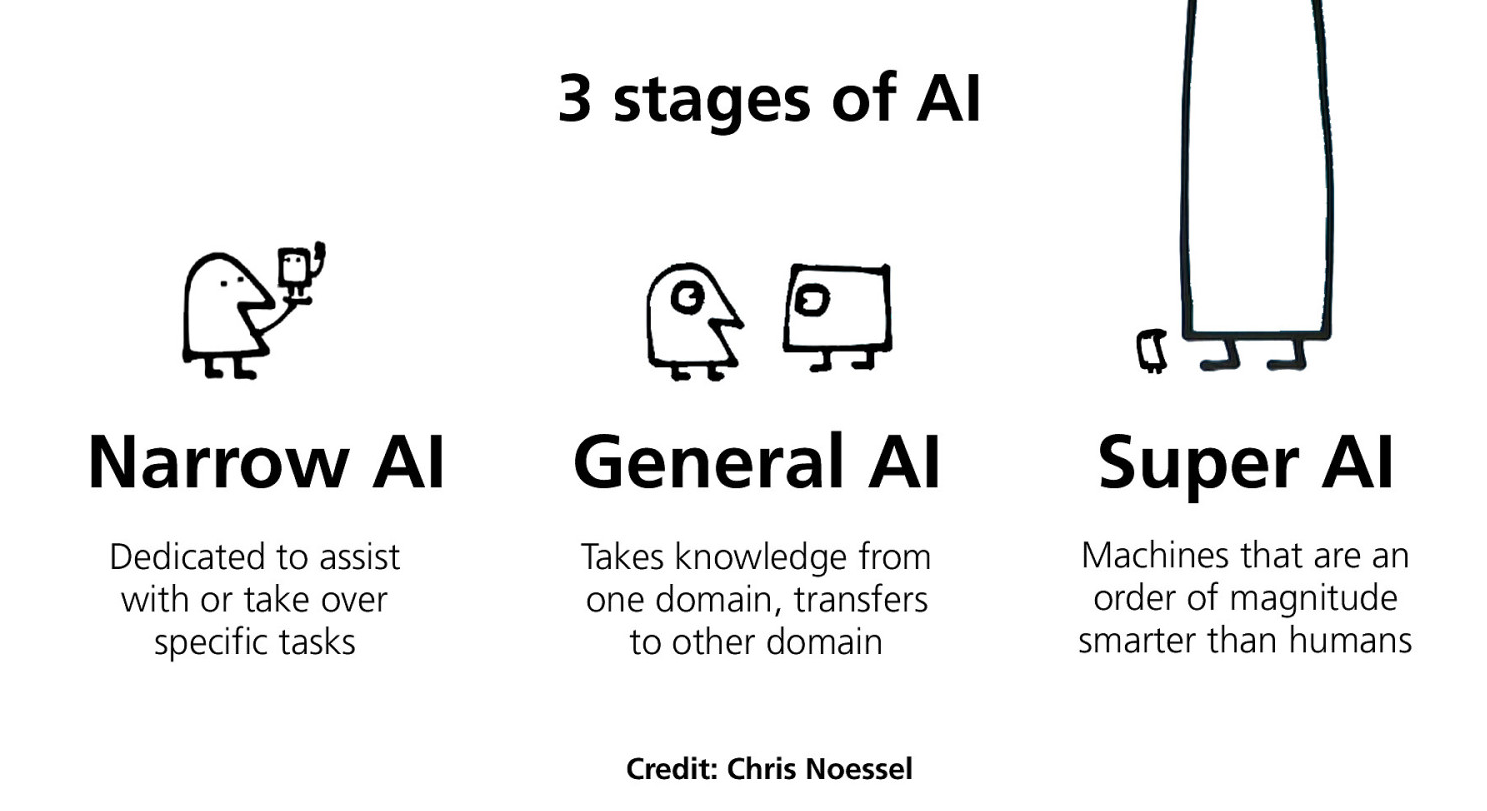
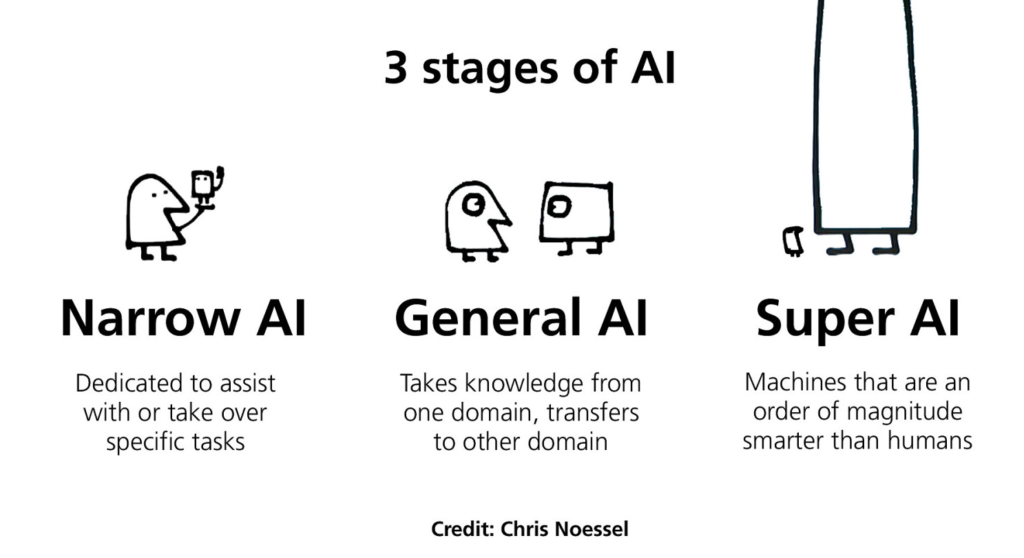
It is important to note that performing those tasks do not tell us how intelligent the computer is. It does not necessarily imply the computer reasons or knows what it is doing. That is why we commonly distinguish AI into 3 subcategories (3 main shades) :
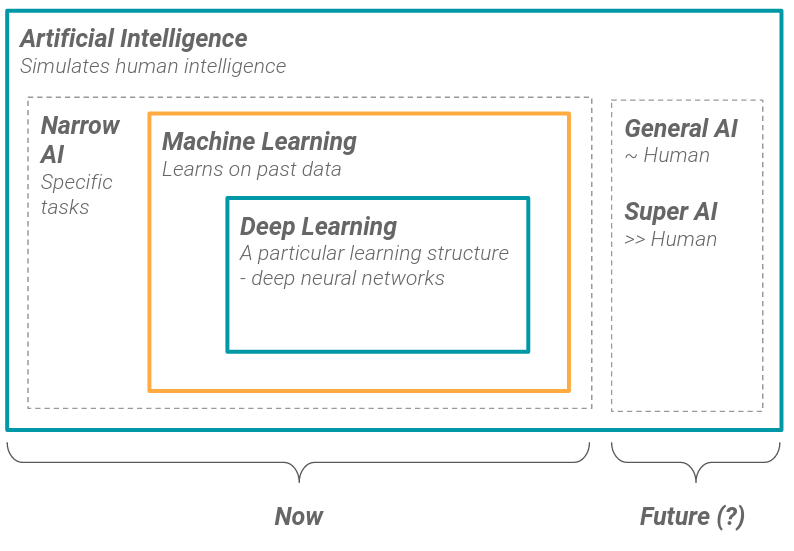
- Narrow AI : accomplishes specific tasks. All Artificial Intelligences today are Narrow.
- General AI : is performant as a human in perception tasks and is capable of reasoning
- Super AI : an AI as performant as all humans combined
What Fuels AI Today?
Data and Machine Learning.
For example a machine learning model that is meant to detect automatically an animal species will learn from millions of animal photos that cats ears are pointy. The model learns this fact by taking in input the image pixels and finding that the pattern of pixels corresponding to the cat’s ear is a good way to distinguish cats from birds, dogs and other species. Another set of features will be picked up by the model to distinguish cats from say red pandas.
There are many algorithms that are capable to pick up statistical patterns, they can be split into two families :
- Shallow learning : for example decision trees, linear regressions
- Deep learning : deep neural networks with many hidden layers
For a semi-technical dive into shallow learning and deep learning you can read these two dedicated blog posts :
- 8 machine learning algorithms explained in human language
- 3 deep learning architectures explained in human language
WHAT IS NOT AI ?
To set the record straight here are a few things that AI is not :
- A proxy of the human brain. Neural Networks are much simpler than the human brain
- A robot with human aspect capable of reasoning
- A know-it-all computer capable of answering any question
- A program capable of predicting the future with 100% accuracy
CONCLUSION
To sum up, today’s AI systems accomplish specific tasks, they are called Narrow AIs. This can already prove extremely useful to wide range of industries and businesses.
Narrow AI’s are mostly based on deep learning which is a subfield of machine learning.
AIs can be combined together to create complex systems such as human-like robots. One such robot can be equipped with the following models :
- A walking model (Reinforcement learning)
- An object and person detection model (Deep learning)
- A face recognition model (Deep learning)
- A reading model (Deep learning)
- A game-playing model (Reinforcement learning)
Instead of one General AI it is a combination of Narrow AIs that makes the robots capacities.
Available data and computation resource are the key factors to the expansion of AI applications across the world. There are two key challenges for AI today :
- The short term challenge is to democratize AI and deploy it at scale in order to help businesses and organizations leverage this incredible technology
- The long term challenge is to develop a General AI capable of reasoning combining mathematical research in the fields of deep learning, graph theory and symbolic AI.